Undo/Redo in React Using XState
I recently came across the need for undo and redo functionality in my app.
The app is an editor of sorts that allows you to add stuff and remove stuff using several different tools and keyboard shortcuts. All implemented using xstate.
It would be great to be able to undo and redo actions taken in the editor! Let's see how we can implement the undo/redo pattern from the Redux docs in XState.
Let's say we have the following machine:
const editorMachine = Machine(
{
id: "editor",
context: {
items: []
},
initial: "normal",
on: {
DELETE_SHAPE: {
actions: ["deleteShape"]
}
},
states: {
normal: {
on: {
TOGGLE_MODE: "turbo",
ADD_SHAPE: {
actions: ["addShape"]
}
}
},
turbo: {
on: {
TOGGLE_MODE: "normal",
ADD_SHAPE: {
actions: ["addThreeShapes"]
}
}
}
}
},
{
actions: {
addShape: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [...ctx.items, e.shape]
}),
addThreeShapes: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [...ctx.items, e.shape, e.shape, e.shape]
}),
deleteShape: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [
...ctx.items.slice(0, e.index),
...ctx.items.slice(e.index + 1)
]
})
}
}
);
Which matches the following visualization:
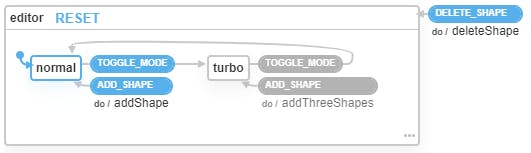
There's basically 2 states:
- Normal, in which you can add 1 shape at a time to the list of items.
- Turbo, in which you can add 3 shapes at a time to the list of items.
In both states you can delete a shape (you pass the shape's list index to the event, e.g. by clicking on it).
To be able to undo/redo our mutations to the items context, we need to do a few things (taken from The Redux Doc on Undo/Redo):
Handling Undo
- Remove the last element from the past.
- Set the present to the element we removed in the previous step.
- Insert the old present state at the beginning of the future.
Handling Redo
- Remove the first element from the future.
- Set the present to the element we removed in the previous step.
- Insert the old present state at the end of the past.
Handling Other Actions
- Insert the present at the end of the past.
- Set the present to the new state after handling the action.
- Clear the future.
Here's what that looks like in our Machine:
const editorMachine = Machine(
{
id: "editor",
context: {
// Keep track of the past
past: [],
// Our present
items: [],
// Keep track of the future
future: []
},
initial: "normal",
states: {
on: {
DELETE_SHAPE: {
// Update the past when we delete a shape
actions: ["updatePast", "deleteShape"]
},
UNDO: {
actions: ["undo"]
},
REDO: {
actions: ["redo"]
}
},
normal: {
on: {
TOGGLE_MODE: "turbo",
ADD_SHAPE: {
// Update the past when we add a shape
actions: ["updatePast", "addShape"]
}
}
},
turbo: {
on: {
TOGGLE_MODE: "normal",
ADD_SHAPE: {
// Update the past when we add 3 shapes
actions: ["updatePast", "addThreeShapes"]
}
}
}
},
},
{
actions: {
addShape: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [...ctx.items, e.shape]
}),
addThreeShapes: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [...ctx.items, e.shape, e.shape, e.shape]
}),
deleteShape: assign({
items: (ctx, e) => [
...ctx.items.slice(0, e.index),
...ctx.items.slice(e.index + 1)
]
}),
// # Handling Other Actions
updatePast: assign({
// 1. Insert the present at the end of the past.
past: ctx => [...ctx.past, ctx.items],
// 2. Set the present to the new state after handling the action.
// ! This happens in the 3 specific actions above
// 3. Clear the future.
future: []
}),
// # Handling Undo
undo: assign(ctx => {
const previous = ctx.past[ctx.past.length - 1];
// 1. Remove the last element from the past.
const newPast = ctx.past.slice(0, ctx.past.length - 1);
return {
past: newPast,
// 2. Set the present to the element we removed in step 1.
items: previous,
// 3. Insert the old present state at the beginning of the future.
future: [ctx.items, ...ctx.future]
};
}),
// # Handling Redo
redo: assign(ctx => {
const next = ctx.future[0];
// 1. Remove the first element from the future.
const newFuture = ctx.future.slice(1);
return {
// 2. Set the present to the element we removed in step 1.
items: next,
// 3. Insert the old present state at the end of the past.
past: [...ctx.past, ctx.items],
future: newFuture
};
})
}
}
);
And that's all! Now we have all the benefits of state machines combined with an undo/redo system on our extended state. We can craft a robust, complex editor (think of all the tools in the Photoshop toolbox) while keeping our undo/redo system simple!
Check out the CodeSandbox for an implemented example.
